We live in a world of trillions of microscopic bugs. Humans are home to an incredible and diverse range of bacteria, fungi and other organisms that live on us, in us, and around us. While you may not see them, tiny bugs are around you every single day. These microscopic bugs live on your skin, in your hair, and on the surface of the objects around you. Here is a guide to the types of microscopic bugs that live on humans.
Eight Legs
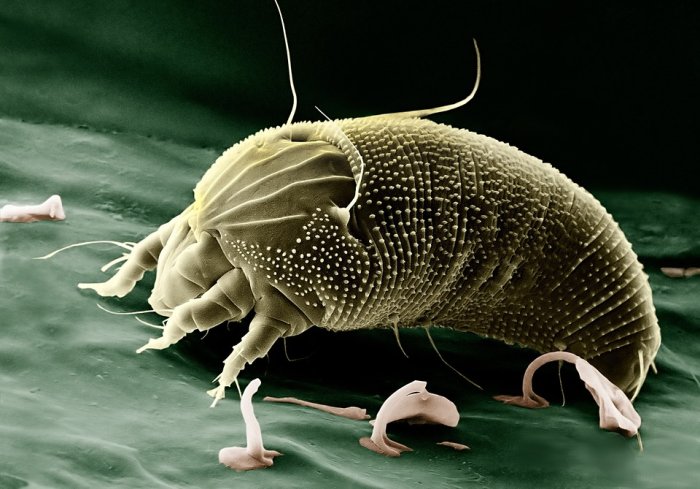
Demodex mites are microscopic, eight-legged parasites that live in or near your hair follicles. They’re typically found in your facial skin, but they can be anywhere on your body. You can get demodex mites from your parents when you’re in the womb, from contact with other people — particularly those who have a lot of facial hair — and from pets. The mites are so small that they can escape detection with the naked eye. The mites live in the oil glands of your hair follicles and the sebaceous glands under your skin.
Living in Hair Follicles
Demodex folliculorum are parasitic mites that live in or near hair follicles. Around 50 percent of people have Demodex folliculorum, and 90% of those people have no signs or symptoms. These mites are not known to spread disease. Demodex folliculorum is one of the two species of Demodex mites that affect humans.
There are several types of mites that feed on human material. Mites are tiny invertebrates belonging to the class Arachnida. They are closely related to ticks and spiders. Mites of medical importance are: Chiggers, scabies, harvest mites, spider mites, red bug bites, and sand flea bites.
We All Have Face Mites!
Face mites are found in the human sebaceous glands and eyelashes. They are different than dust mites which live in mattresses, pillows, sofas, carpets and other soft furnishings. Mites that live on the face are thought to be transmitted from person to person by direct physical contact. This means that a mite can’t jump from person to person, but it can live on a person’s body for about a week without coming into contact with anyone else.
Demodex brevis, also known as the short-nosed Demodex mite, live on humans and feed on skin cells. They don’t create any problems for healthy people, but people who have a weakened immune system can experience problems from a Demodex infestation. The most common signs of a Demodex infestation include red, sore, and itchy skin.
In the U.S., there are over 1,000 species of mites. The most common mite that lives on humans is the house dust mite, which is found in most homes across the country. You can find mites on other animals, but they do not typically feed on humans. House dust mites live in your home and feast on dead skin cells. They’re not harmful to humans but can cause mild allergic reactions.